If you celebrated National Periodic Table Day with the World’s #1 Source of Research-Based Content, The Daily Top 10, you will surely know the Top 10 Reasons Why We Celebrate National Periodic Table Day. But, are you still curious to learn more about the building blocks of the universe? How much do you know about this essential tool? In this article, we are going to discuss the Top 10 Most Important Facts About the Periodic Table of Elements.
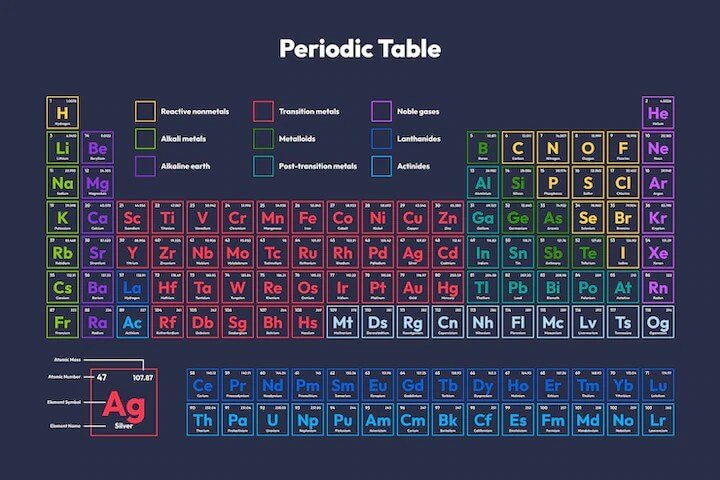
Do you know the Top 10 Most Common and Abundant Elements in the World? However, the periodic table is arranged in order of increasing atomic number, which is the number of protons in an atom’s nucleus. The elements are also grouped based on their chemical properties. For example, the metals are found on the left side of the table, while the nonmetals are on the right. A periodic table is a powerful tool for understanding the behavior of atoms and molecules. It can be used to predict how elements will react with one another and to understand why certain reactions occur.
So, in this context, the periodic table is associated with some interesting facts and here we go to find the Top 10 Most Important Facts About the Periodic Table of Elements.
What is the Most Important Fact About the Periodic Table of Elements?
Can you remember that we recently shared with you the Top 10 Deadliest and Dangerous Substances No one Can Hide From? The periodic table is a chart that organizes chemical elements in a useful and logical way. Unfortunately, for many people, the periodic table is something they were monotonously asked to memorize as students. But the truth is, this little chart is an indispensable tool for scientists everywhere.

Here are some interesting and also little-known facts about the periodic table of chemistry, written for both science enthusiasts and all students studying chemistry. Let’s have a look at these facts from the tenth contender, before paying attention to the Most Important Fact About the Periodic Table of Elements.
TOP 10: 4 Recently Named Elements
Last December, four new elements – with atomic numbers 113, 115, 117, and 118 – earned their place on the periodic table, as stated in Science. After the declaration is over, those names are finally official and three of the elements are named after the positions of scientific institutions: Tennessee (Tennessee), Nihonium (Japan), and Moscovium (Moscow). Those four elements complete the seventh row of the table.
Yuri Oganessian, professor of nuclear physics at the Joint Nuclear Research Institute, inspired the fourth, Oganesson. Nihonium, discovered by a Japanese team, means “Land of the Rising Sun,” while Moscovium and Tennessine are named for the location near the labs where they were discovered (Moscow and Tennessee, of course). Traditionally, the right to give an element’s name rests with its discoverer, although IUPAC does, especially with different laboratories often vying for the top spot, not always.
TOP 9: Technetium is the Lightest and First Artificially Produced Element

According to Wikipedia, the first element not found in nature but synthesized was Technetium in 1937. This discovery fills a gap in the periodic table and the lack of stable technetium isotopes explains that technetium does not exist naturally on Earth. Since the half-life of the longest-lived technetium isotope, 97Tc, is 4.21 million years, technetium did not exist during the formation of the Earth. Only traces are present of technetium that occurs naturally in the Earth’s crust.
Amidst as stated in ABC, Technetium is the lightest radioactive element on the periodic table and its isotopes decay into a variety of other elements including stable ruthenium. It was discovered in 1937 by Carlo Perrier and Emilio Segre, and its discovery had significant implications for nuclear physics research. Technetium has no stable isotopes, which means that all of its isotopes are radioactive, making it an important tool in medical diagnostics.
TOP 8: Elements Classified as Metalloids and Non-Metalloids
Metalloids are sometimes called semi-metals because the term semimetal has a different meaning in medicines than it does in chemistry. As the Physical Metals say, the term metalloid was originally called nonmetals. Typically, metalloids are good drivers of electricity and they have a metallic appearance also. Chemically, they mainly act as nonmetals while they and their mixes are used in composites, natural agents, catalysts, honey retardants, glass, optical and optoelectronic storage, fireworks, etc.
Metalloids and nonmetals lie on either side of the dividing line between substances and nonmetals. This can be set up, in various configurations, on several periodic tables. Elements at the undermost left sect of the line generally parade adding metallic behavior the upper right elements show adding non-metallicity. When represented as a regular staircase, the elements with the topmost critical temperature for their group( Li, Be, Al, Ge, Sb, Po) are directly below the line.
TOP 7: Elements Classified as Metals and Non-Metals
The periodic table includes elements that are metals, those that are non-metals, and elements that have properties moderate between the two groups(metalloids), according to Angelo Education Faculty. Metals are hard metals – such as solids with high electrical and thermal conductivity valuations as well as melting and boiling points. Nonmetals tend to be gentle, generally colored elements.
They are formed as solid, liquid, or gaseous conformations and have lower melting and boiling points than utmost metals, and are generally not sound operators of electricity. The utmost elements are metals as they are broken up from nonmetals through carbon, phosphorus, selenium, iodine, and radon, in the periodic table. These elements and those to their right are nonmetals while nonmetals show off on the right side of the periodic table, except hydrogen. Non-metallic elements are hydrogen, carbon, nitrogen, phosphorus, oxygen, sulfur, selenium, all halogens, and noble feasts.
TOP 6: Elements Grouped According to Chemical Groups

According to Chem Libretexts, the periodic table was arranged according to the rudiments with the most analogous groups and deposited in the identical group. A group is a perpendicular column of the periodic table and all of the 1A rudiments retain one valence electron. This is what causes these rudiments to respond in equal ways as the other members of the family.
The rudiments in 1A are each truly reactive and form mixes in the same proportions with analogous groups with other rudiments. Also, For illustration, Group 2A is known as an alkaline earth substance. Mendeleev arranged the table according to the rudiments with the most similar parcels that were in the same group on the periodic table. This group contains largely active-metallic rudiments and it’s important to note that several other significant groups on the periodic table are by group name.
TOP 5: 118 Elements Divided into Groups and Periods
The periodic table of rudiments is organized by atomic number and it determines the identity of an element and how multitudinous electrons compass it. It has seven rows and 18 columns, as stated in Libre Texts. Moreover, the period number of an element indicates how numerous of its energy situations produce electrons.
The arrangement of electrons in an element’s outermost jacket determines its chemical behavior and also, and it’s determined by the number of electrons in its outermost shell. A periodic table is combined in order of adding atomic numbers. While the rudiments having analogous chemical groups naturally line up in the same column(group).
TOP 4: Batteries Used to Calculate Elements Weight

To define the weight of each of the 63 given rudiments of that time, scientists passed currents through several results. The purpose was to resolve them up into the titles of specific rudiments and then, according to RSC, to separate the titles, scientists used batteries. The reason behind that is the batteries’ opposition would make titles of one element move in one direction and others in another. Then the titles were collected independently and they ladened during this process.
Inside every battery, there are four factors: two electrodes, a division, and an electrolyte. For the periodic table, they concentrated on the rudiments that make up the cathode, anode, and carrier. Generally, batteries are stores of energy created by the commerce of different rudiments at the atomic position.
TOP 3: Elements Arranged by Accelerating Value of Atomic Numbers
In the modern periodic table, the elements are listed in order of accelerating atomic number. Based on the data we gathered from Chem Libretexts, the atomic Value is the Value of protons in the nexus of a snippet. The number of protons outlines the sameness of an element and the number of protons determines how multitudinous electrons compass the nexus, and it’s the strategy of these electrons that determines the ultimate chemical behavior of an element.
In a periodic table, concerted in order of adding atomic value, elements keeping correspondent chemical properties constitutionally line up in the identical column. For example, all of the rudiments in Group 1A are fairly soft essence, reply violently with water, and form 1 counts; all of the rudiments in Group 8A are unreactive, monatomic feasts at Normal temperature, etc. In other terms, there is a periodic repetition of the parcels of the chemical rudiments with adding mass.
TOP 2: Listed All the Known Elements in the Universe

There are around 94 rudiments on the periodic table that change in nature. All of the other rudiments are strictly mortal-made and some sources state farther rudiments are natural because heavy rudiments may transition between rudiments as they witness radioactive decay. Technetium was the first artificially produced element as it’s the lightest element that has only radioactive isotopes( none are stable).
The ultimate of the elements on the periodic table is the essence. The alkali essence, earthing earth, introductory essence, transition essence, lanthanides, and actinides all are clusters of metals. The present periodic table has space for 118 rudiments, as Libre Texts says. Rudiments aren’t caught on or created in order of infinitesimal number.
TOP 1: Dimitry Mendeleev is the Founder of the Periodic Table

Dimitry Mendeleev is formerly regarded as the father of the ultramodern periodic table. He’s a Russian chemist who introduced the periodic table on 6th March 1869 at a Russian chemical society. Though he contributed the credit for the design of this periodic table, his table was not regarded as the first endeavor to arrange the elements coinciding with periodic properties, according to ASBMB.
It’s because in 1864, Julius Lotar Meyer, a German chemist who also worked with Dimitry, published a periodic table. It depicted the placement of 28 elements and then, Julius developed his fuller periodic table unassisted. But he admitted Dimitry’s work is great and accordingly, Dimitry Mendeleev being the Founder of the Periodic Table is the Most Important Fact About the Periodic Table of Elements.
What are the Most Important Facts About the Periodic Table of Elements?
The periodic table of elements is a graphical representation of chemical elements. It’s converted according to their atomic figures so that chemical rudiments with analogous atoms are in the same column. Also, it is an important tool for making out the world around us. It can be used to identify elements, forecast their properties, and decide the connections between elements.
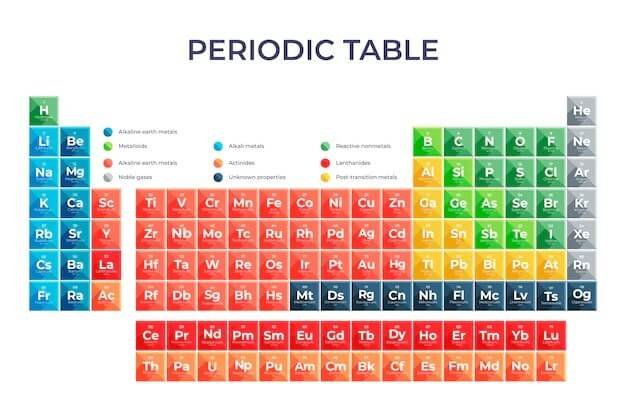
Here are the Top 10 Most Important Facts About the Periodic Table of Elements:
- Dimitry Mendeleev is the Founder of the Periodic Table
- Listed All the Known Elements in the Universe
- Elements Arranged by Accelerating Value of Atomic Numbers
- Batteries Used to Calculate Elements Weight
- 118 Elements Divided into Groups and Periods
- Elements Grouped According to Chemical Groups
- Elements Classified as Metals and Non-Metals
- Elements Classified as Metalloids and Non-Metalloids
- Technetium is the Lightest and First Artificially Produced Element
- 4 Recently Named Elements
In summary, the periodic table is important since it is organized to provide a wealth of information about the elements and how they relate to each other in one easy-to-use reference. If you need more worth reading education-related topics like this, browse in our Education-Work-Facts category for the Top 10 Most Common Mental Health Issues in College Students, the Top 10 Reasons Why You Should Study Abroad in Australia, and the Top 10 Best Strategic Ways to Recover From Burnout Faster. Furthermore, want us to be your partner? Send us an email or hit the contact form and send us your message!


Top 10 Best Birthday Gift Ideas for People Born in February
Top 10 Best Tech, Web3, and Blockchain News & Trends in 2023
Top 10 Most Expensive Super Bowl Ads of All Time (Updated)
Top 10 Best & Most Popular Universities in India (Updated)
Top 10 Richest Countries in the World by GDP Per Capita (Updated)
Top 10 Best Ways to Make Money Online Without Investment (Updated)